BFS는 DFS와 같이 탐색을 주로하는 알고리즘입니다.
이와 관련한 설명은 DFS 설명할 때 같이 했으니 보고오시는 것을 추천드립니다.
https://ris-blog.tistory.com/22
DFS (Depth First Search) 깊이 우선 탐색 설명
DFS는 우선 제목에 나와있듯이 '탐색'하는 알고리즘입니다.고로 이는 순서가 있는 혹은 방향이 있는 자료구조에서 쓰이며이는 선형 자료구조라고 합니다. 우선 DFS의 탐색 과정을 봅시다.위의 사
ris-blog.tistory.com
바로 BFS의 작동 순서를 표시하겠습니다.
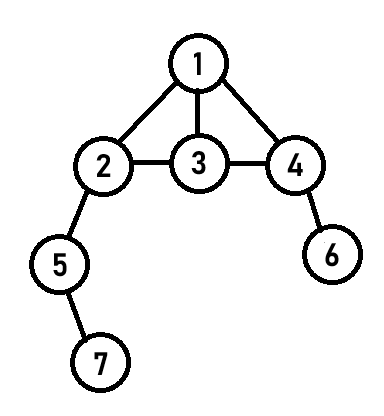
노드 안의 숫자는 순서를 나타냅니다.
이 그림에서 DFS와 BFS의 차이가 나타납니다.
DFS는 하나의 노드를 끝까지 탐색한다면 BFS는 각 노드를 한번씩 탐색합니다.
이해를 돕기위해 예를 들자면 DFS는 드라마를 끝까지 보고 다른 드라마를 본다면 BFS는 각 드라마를 1편씩만 보고 다른 것을 보는 것입니다.
그럼 바로 코드로 구현해보겠습니다.
주석 O
n, m = map(int ,input().split()) # n : node, m = 간선
visited = []
graph = {}
# 양방향 그래프일 때만
# 인접 리스트
for i in range(m):
f, s = map(int ,input().split())
if not f in graph:
graph[f] = []
if not s in graph:
graph[s] = []
graph[f].append(s)
graph[s].append(f)
def BFS(graph, start, visited): # graph : 자료, start : 시작지점, visited : 다녀간 노드 리스트
queue = [start] # queue 사용
while queue: # 모든 노드가 탐색될 때까지
node = queue.pop(0) # queue에 있는 하나의 노드를 뺌
if node not in visited: # 해당 노드가 다녀간 곳이 아니라면
print(node) # 다녀갔다는 것을 표시하고
visited.append(node) # 다녀갔음을 기록한다
for neighbor in graph[node]: # 저장하는 방식을 인접 리스트로 저장했기에 연결된 노드들을 확인 가능
if neighbor not in visited: # DFS와 다르게 해당 노드만 탐색하고 주변 노드 탐색
queue.append(neighbor) # 반복
BFS(graph, 1, visited) # 오름차순의 리스트라서주석 X
n, m = map(int ,input().split())
visited = []
graph = {}
for i in range(m):
f, s = map(int ,input().split())
if not f in graph:
graph[f] = []
if not s in graph:
graph[s] = []
graph[f].append(s)
graph[s].append(f)
def BFS(graph, start, visited):
queue = [start]
while queue:
node = queue.pop(0)
if node not in visited:
print(node)
visited.append(node)
for neighbor in graph[node]:
if neighbor not in visited:
queue.append(neighbor)
BFS(graph, 1, visited)'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Graph에 대해서 (0) | 2025.03.23 |
|---|---|
| DFS (Depth First Search) 깊이 우선 탐색 설명 (3) | 2024.11.02 |
| 합병 정렬(Merge sort) 개념 간단 설명 (1) | 2024.09.23 |
| Swap 구현 [python, c++] (2) | 2024.07.24 |


